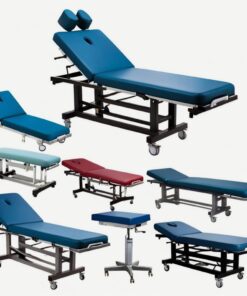
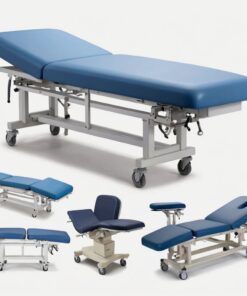
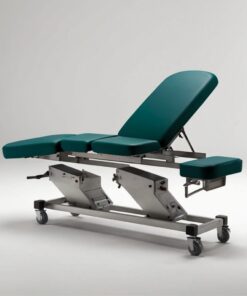
Standard Cholera Bed
R3,946.00 Ex VAT
MedQ PPE Supplies represents over 40 manufacturers and suppliers of PPE, safety shoes, safety boots, Helmets. We take pride in personalized delivery focusing on the main African countries. We have offices and warehouses in Johannesburg, Durban, Limpopo. We hold over 5,000 different products in stock. Our well trained sales staff are on hand to receive your calls or emailed inquiries.
In hospitals, various types of beds are used to accommodate different patient needs and treatment requirements. Below are the main types of hospital beds and their specific uses:
1. Manual Hospital Bed
- Uses: Manual hospital beds require caregivers to use hand cranks to adjust the bed’s position. These beds are cost-effective and suitable for patients who do not need frequent position adjustments.
- Applications: Typically used in smaller clinics or home care settings where there is less need for frequent adjustment and mobility.
2. Electric Hospital Bed
- Uses: These beds can be adjusted using electric controls, allowing the patient or caregiver to raise or lower the bed’s head, foot, or height easily.
- Applications: Commonly used in hospitals and long-term care facilities to provide comfort and easy mobility for both patients and staff.
3. Semi-Electric Bed
- Uses: Semi-electric beds combine manual and electric functions. The head and foot sections are adjusted electrically, but the height of the bed is controlled manually.
- Applications: Used for patients who require some adjustments but do not need full electrical functionality.
4. ICU (Intensive Care Unit) Bed
- Uses: ICU beds are equipped with advanced features like built-in monitors, air pressure mattresses to prevent bedsores, and motorized controls to allow for frequent position changes. They often include side rails and emergency CPR functions.
- Applications: Used in intensive care units for critically ill or injured patients requiring close monitoring and care.
5. Low Bed
- Uses: Low beds are designed closer to the ground to reduce the risk of falls, especially for patients with mobility issues or those prone to rolling out of bed.
- Applications: Ideal for elderly patients or patients with mental health concerns who may be at higher risk of injury from falling out of bed.
6. Bariatric Bed
- Uses: Bariatric beds are specifically designed for overweight or obese patients, offering higher weight capacities and wider sleeping surfaces.
- Applications: Used in hospitals or care settings that accommodate larger patients who require extra support.
7. Air Mattress Bed
- Uses: Air mattress beds (alternating pressure or low air loss) help prevent bedsores and promote proper circulation by regularly redistributing the patient’s weight.
- Applications: Commonly used for patients who are bedridden for long periods or are at high risk for pressure ulcers.
8. Gatch Bed
- Uses: A Gatch bed is a manual hospital bed where the backrest, knee rest, and footrest can be adjusted via hand cranks. It is an older style of hospital bed but is still used in some care settings.
- Applications: Used in environments where electrical beds are not feasible, often in smaller or under-resourced medical facilities.
9. Rehabilitation Bed
- Uses: These beds are designed to assist patients undergoing physical therapy or recovery from surgery, offering adjustable positioning to aid in rehabilitation.
- Applications: Used in rehab centers or hospital wards where mobility and ease of access for therapists and caregivers are crucial.
10. Pediatric Bed
- Uses: Pediatric beds are specifically designed for children. They are smaller in size and often have additional safety features like high side rails to prevent falls.
- Applications: Used in pediatric wards for the care of infants, toddlers, and children who need special accommodations in hospital settings.
11. Stretchers (Transport Bed)
- Uses: Stretchers are lightweight, mobile beds that can be easily moved. They are used for transporting patients between different areas of the hospital or during emergency situations.
- Applications: Used in emergency rooms, operating rooms, or for transporting patients for diagnostic tests or procedures.
12. Adjustable Bed
- Uses: Similar to electric beds, adjustable beds allow for the modification of the head, foot, and overall height positions. These beds are typically used to improve comfort and aid in mobility.
- Applications: Often used in long-term care facilities or home care settings for patients needing additional comfort during extended recovery periods.
These beds play a critical role in ensuring patient safety, comfort, and the efficiency of care provided in medical settings.
RUBBER HOUSEHOLD GLOVE
Related products
Examination bed
Examination bed
Examination bed
Examination bed
Examination bed
Examination bed
Examination bed
Examination bed